 With the need to access information and files in real time, instantly and from any location and from any computer, cloud computing was developed. While there are advantages and disadvantages associated with most business models, it is largely up to organization to decide whether this system is right for their industry.
With the need to access information and files in real time, instantly and from any location and from any computer, cloud computing was developed. While there are advantages and disadvantages associated with most business models, it is largely up to organization to decide whether this system is right for their industry.
What exactly is cloud computing?
Cloud computing refers to the practice of transitioning computer services such as computation or data storage to multiple redundant offsite locations available on the Internet, which allows application software to be operated using internet-enabled devices.
Cloud computing meaning
Cloud computing is defined as a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources rather than having local servers or personal devices to handle applications. It is comparable to grid computing, a type of computing where unused processing cycles of all computers in a network are harnesses to solve problems too intensive for any stand-alone machine.
The name cloud was inspired by the symbol that’s often used to represent the Internet in flowcharts and diagrams. Clouds are distributed technology platforms that leverage sophisticated technology innovations to provide highly scalable and resilient environments that can be remotely utilized by organizations in a multitude of powerful ways.
What is cloud computing in simple terms?
In simple terms it means storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of your computer’s hard drive. Cloud Computing is the use of hardware and software to deliver a service over a network (typically the Internet). With this service users can access files and use applications from any device that can access the Internet.
Cloud computing and storage solutions provide users and organization with various capabilities to store and process their data in third-party data centers. With cloud computing, multiple users can access a single server to retrieve and update their data without purchasing licenses for different applications.
What makes cloud computing different?
- It is managed
- It’s “on-demand” (available on-demand and often bought on a “pay-as-you go” or subscription basis.)
- It’s public or private
- It is virtual
- It is flexible and scalable
- It can be secure and affordable
- It can be affordable
- It is open (or closed)
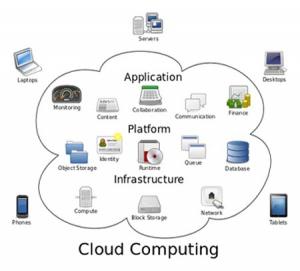
Types of cloud computing Service models
Cloud is usually defined in one of three ways: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) or software as a service (SaaS).
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Refers to the hosting of a cloud service. It is a form of cloud computing that provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. IaaS Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Joyent.
- Cloud-based applications—or software as a service (SaaS)- is where cloud developers play. It means you use a complete application running on someone else’s system. SaaS is sometimes referred to as “on-demand software” and is usually priced on a pay-per-use basis or using a subscription fee.Web-based email and Google Documents are perhaps the best-known examples.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)- is cloud-based delivery of software. In this models, cloud providers deliver a computing platform, typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. Salesforceand the Google App Engine are examples of PaaS.
Deployment models:
- Private cloud infrastructure operated solely for a single organization, whether managed internally or by a third-party, and hosted either internally or externally.
- Public cloud, when the services are rendered over a network that is open for public. Users don’t need to purchase hardware, software or supporting infrastructure, which is owned and managed by providers.
- Hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more clouds (private, community or public) that remain distinct entities but are bound together, offering the benefits of multiple deployment models.
Some of Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Advantages
- Cost Savings
- Reliability
- simplifies the process data backup and recovery
- Easy to Manage
- Faster Deployment and Simple Integration
- Offers almost unlimited storage capacity
- Convenience and Continuous Availability
- Disaster recovery (DR) solution
Disadvantages
- Downtime
- Stored data might not be secure
- Vendor Lock-In
- Less control over the hardware and the software
- Vulnerable to hackers and unwanted users
- Doesn’t work well with low-speed connections
Also, check video to understand What is Cloud Computing
I believe this post is able to explain what is cloud computing in simple terms. Like to read further then check the useful links below.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
http://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/in/en/what-is-cloud-computing.html

